pH-sensitive alginate hydrogel for synergistic anti-infection
Abstract: This work designed a pH-sensitive sodium alginate hydrogel for combating bacterial infection caused by tissue damage. The antibacterial hydrogels were prepared using sodium alginate, citric acid, and vancomycin by one- step in situ method. Vancomycin (Van) was loaded into hydrogels via reversible imine bonds for controlled drug delivery. The morphology, swelling properties, and antibacterial activity of hydrogel were characterized. The hydrogel shown strong water absorbent behavior and pH-dependent performance. The result under weak acid conditions, the drug release rate of van-loaded gel was faster than neutral and alkaline conditions and followed zero-order kinetic release model, and the cumulative release amount could reach 86.7 % over 320 min. The van- loaded gel had highly effective antibacterial activity in a weak acid environment, the combination of citric acid and vancomycin had a synergistic therapeutic effect for acute infection. The drug-loaded hydrogel shows good biocompatibility. Compared with gauze, the drug-loaded hydrogel exhibited good coagulation properties, high platelet adhesion, high fluid absorption capacity, and proper balance of fluid on the wound bed. This work proposed this simple alginate-based drug delivery system has potential applications in the field of clinical treatment of infections.
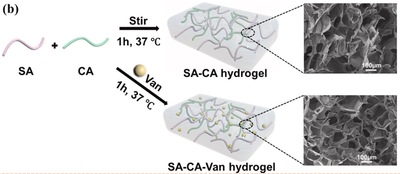
Zhang, Jiaqi, et al. pH-sensitive alginate hydrogel for synergistic anti-infection. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 222, 1723-1733.