High-Yield of Nucleic Acid Adsorption via Poly(Vinyl Alcohol-co-Ethylene) Nanofiber-Based Anion-Exchange Chitosan Aerogel Membrane with Controllable Porosity
ABSTRACT: Due to the fast degradation time and low storage temperature of nucleic acid, a simple, fast, and highly efficient adsorption process is imperious for the extraction of nucleic acid molecules. In this article, a poly(vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene) (EVOH) nanofiber-based and polyethyleneimine (PEI)-modified chitosan (ENPC) aerogel with high static adsorption capacity of RNA and DNA molecules (812 and 867 mg g−1, respectively) is proved for enormous potential in adsorption capacity for nucleic acid extraction. A relation between adsorption capacity and the physical morphology of ENPC aerogel membrane is demonstrated with the controllable factors such as chemical components, freeze-drying temperature, pH value of the nucleic acid solution, and membrane density. The mechanism of the anion-exchange adsorption process of nucleic acid is analyzed and fitted well with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm (monolayer adsorption). The as-obtained ENPC aerogel in the form of a membrane with self-cleaning and flexible properties can be easily tailored and widely utilized in a convenient and efficient extraction process of nucleic acids in both industrial and experimental levels.
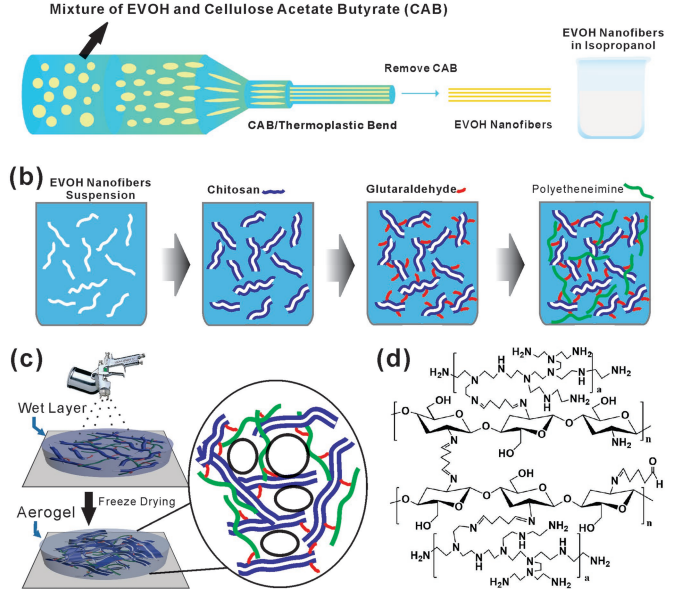
Jia Xu, et al. High‐Yield of Nucleic Acid Adsorption via Poly (Vinyl Alcohol‐co‐Ethylene) Nanofiber‐Based Anion‐Exchange Chitosan Aerogel Membrane with Controllable Porosity[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2022, 2200613.