Synergistically photothermal Au Nanoprisms@MXene enable adaptive solar modulation of HA-PNIPAM hydrogels for smart window
ABSTRACT:Smart windows are highly desired as emerging optical devices based on appealing sunlight modulation, however, some prevailing limitations remain with low photothermal conversion and narrow spectral adjusting ranges, which drastically restrict energy-saving performance. Herein, a strategically designed smart window achieves significant breakthroughs, containing photothermal fillers of Au nanoprisms (AuNPRs) hybrid MXene nanosheets, and copolymerized thermochromic poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-doped hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels. By harness of AuNPR@MXene nanocomposites as photo-trapped nanoheaters, stimulating thermo-responsive behaviors of hydrogels boosts solar transmittance switching. The compelling photothermal features depend on the amalgamation: thermoplasmonic effect of AuNPRs, broad-band-absorbed AuNPRs endowed by MXene, and thermal conductivity from AuNPRs to MXene, generating synergistic effects. We maximize the advancing transmittance regulation by controlling the proportion gain of HA to increase hydrogen-bonded interaction. The resulting device with low-loadings AuNPR@MXene composites (0.9 wt% and 0.98 vol%) is capable of allowing 78 % of the maximum visible light through before thermochromism and blocking 98.04 % of sunlight penetration when photothermal stimulation. Besides, outdoor measurements show an achievable great indoor temperature drop of about 7 ◦C only 30 min irradiation, and a skin-cooling performance in the wearable, illustrating the potential of adaptive solar modulation application.
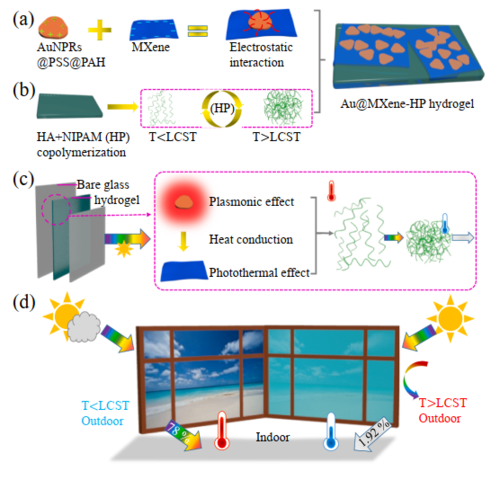
Li Yingying, et al. Synergistically Photothermal Au Nanoprisms@ MXene Enable Adaptive Solar Modulation of HA-PNIPAM Hydrogels for Smart Window. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 141299.