Highly Conductive, Ultrastrong, and Flexible Wet-Spun PEDOT:PSS/Ionic Liquid Fibers for Wearable Electronics
Abstract:Conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) fibers with high electrical conductivity, flexibility, and robustness are urgently needed for constructing wearable fiber-based electronics. In this study, the highly conductive (4288 S/cm), ultrastrong (a high tensile strength of 956 MPa), and flexible (a low Young’s modulus of 3.8 GPa) PEDOT:PSS/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide (EMIM:DCA) (P/ED) fiber was prepared by wet-spinning and a subsequent H2SO4-immersion–drawing process. As far as we know, this is the best performance of the PEDOT:PSS fiber reported so far. The structure and conformation of the P/ED fiber were characterized by FESEM, XPS, Raman spectroscopy, UV–vis–NIR spectroscopy, and WAXS. The results show that the high performances of the P/ED fiber are mainly attributed to the massive removal of PSS and high degree of crystallinity (87.9%) and orientation (0.71) of PEDOT caused by the synergistic effect of the ionic liquid, concentrated sulfuric acid, and high stretching. Besides, the P/ED fiber shows a small bending radius of 0.1 mm, and the conductivity of the P/ED fiber is nearly unchanged after 1000 repeated cycles of bending and humidity changes within 50–90%. Based on this, various P/ED fiber-based devices including the circuit connection wire, thermoelectric power generator, and temperature sensor were constructed, demonstrating its wide applications for constructing flexible and wearable electronics.
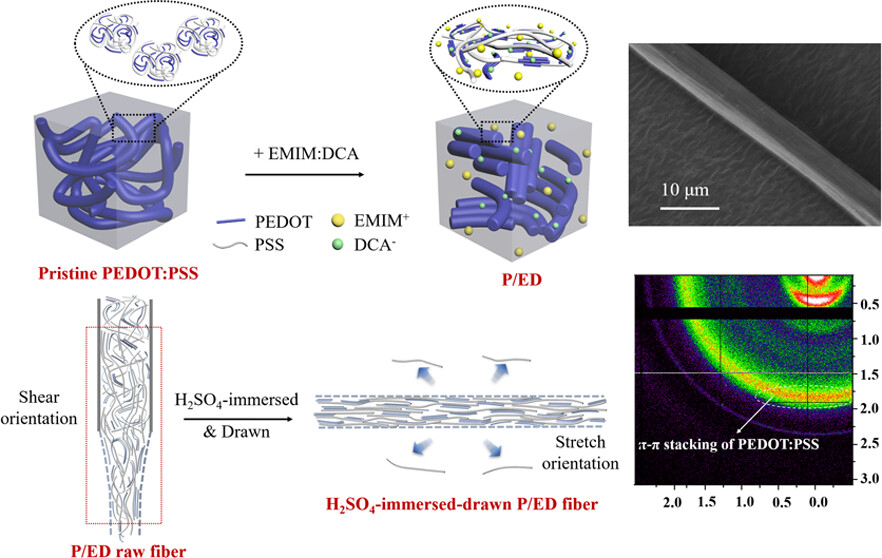
Chen Huijun, et al. Highly Conductive, Ultrastrong, and Flexible Wet-Spun PEDOT: PSS/Ionic Liquid Fibers for Wearable Electronics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15, 20346-20357.