Coupling nano-redox carbon dots with nontraditional AIE-polysaccharides on a smart fabric for healthcare sensing systems
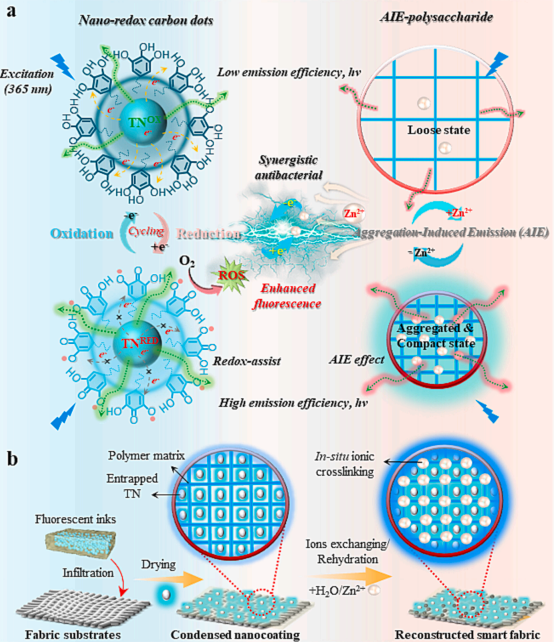
Creating bio-based fluorescent probes with visual-sensing abilities and anti-infection performance is highly desirable but remains challenging. Herein, a multifunctional dual-responsive biopolymeric nanocoating has been designed with synergistically enhanced fluorescent and antibacterial properties that simply implemented by the combination of tannic acid rooted carbon dots (TN, redox-sensitive) and alginate-zinc complex (SA-Zn, ionic sensitive) possessing the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics. The mussel-inspired catechol groups and alginate-metal aggregates afford great film-forming abilities on diverse substrates while the entrapped TN enable manipulation of the redox-dependent fluorescent and antibacterial properties via gener ating reactive free radicals (ROS). The concept of facile pre-sensing and treatment towards in-home sensing application has been perfectly realized on a commercial fabric wipe, demonstrating excellent detection capa bilities for biological molecules (e.g., H2O2 and metal cations) and synergistically enhanced antibacterial per formance. Therefore, bridging the nano-redox carbon dots with nontraditional luminescent polysaccharides can provide enormous potential into advanced fluorescent materials for emerging healthcare applications.
Xianzhu Yang, Kun Yan, Chenguang Yang, Dong Wang, Coupling nano-redox carbon dots with nontraditional AIE-polysaccharides on a smart fabric for healthcare sensing systems, Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 147402.